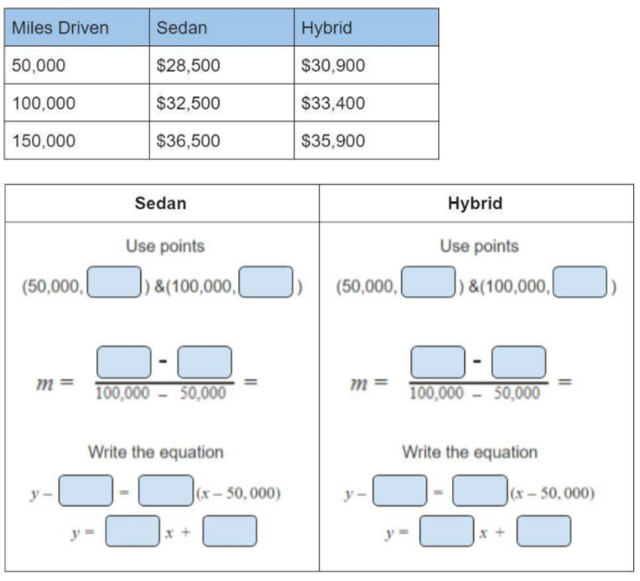
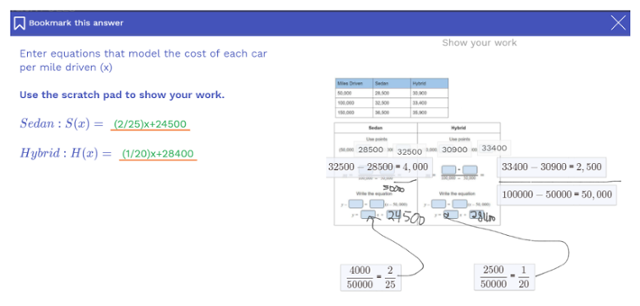
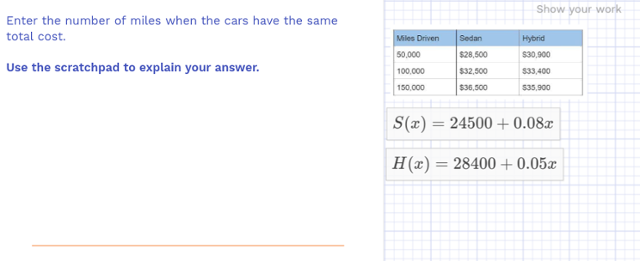
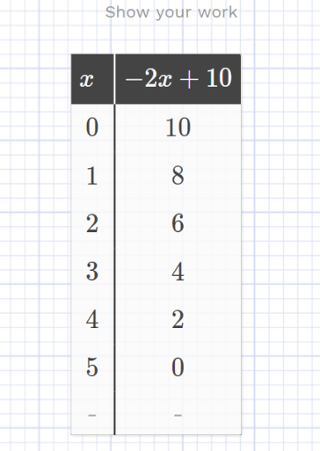
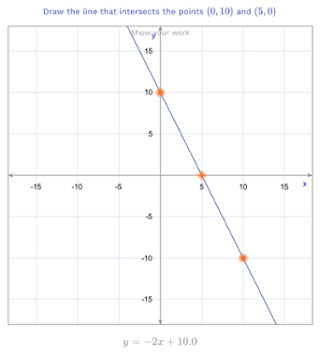
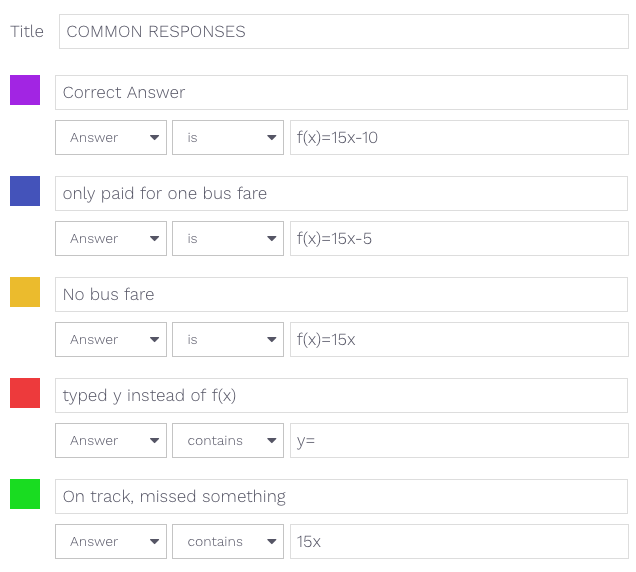
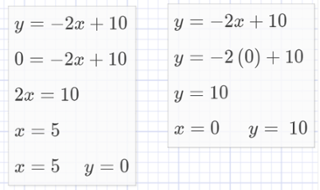As Dr. Robert Siegler and his colleagues found:
“A child’s knowledge of fractions in fifth grade predicts performance in high-school math classes, even after controlling for IQ, reading achievement, working memory, family income and education, and knowledge of whole numbers.”
Fractions: The new frontier for theories of numerical development.
— 2012, Siegler, R. S., Fazio, L. K., Bailey, D. H., & Zhou, X
With a slew of similar findings, it is clear that knowledge of fractions matter. The National Math Panel said it clearly in 2008: “…knowledge of fractions is the most important foundational skill not developed among American students.” Lack of this foundational skill remains equally evident in recent national testing. And yet, imagine the difference it would make if you could ensure that all students had the fluency with rational numbers we know they need to succeed.
Woot Math supports you in making this difference. Teachers that use Woot Math report that it consistently increases both confidence and mastery of rational numbers. In only a few hours of use, teachers see measurable improvements in student performance. Here are a few specific ways that Woot Math’s personalized learning platform can help you ensure your students have the foundation they need to succeed.
We Support You In Your Instruction
Woot Math Adaptive Practice is designed to support a range of implementations. You can assign topics as part of an in-class rotation, for 1-on-1 instruction, or for further practice. The learning platform interleaves short-form instructional videos with engaging interactive problems. An easy to use teacher dashboard is provided so that you can monitor each student‘s progress, report on outcomes, and assign new topics.
Woot Math typically recommends two to four sessions per week, 20 to 30 minutes per session (learn more about our implementation guidelines for
elementary school and
middle school students).
Content Is a Key Differentiator
Woot Math leverages learning sciences’ leading research on teaching rational numbers. “Adaptive technology can only be effective if it leverages quality supplemental content,” says Krista Marks, Woot Math CEO in
Fractions Unlocked: Why Fractions Matter and how technology can help. Our fraction content is informed by decades of research in fraction education from organizations like the
Rational Number Project. With funding from the
National Science Foundation, we have
demonstrated efficacy and effectiveness using Woot Math.
Digital Manipulatives Build Fluency
The ability to work with digital models has proven effective in developing conceptual understanding of fractions. Students need to experience making connections among different representations in order for them to make sense of fractions. In Woot Math, students are exposed to a wide variety of models, including fraction circles, fraction bars, number lines, set models and more. As students gain experience and exposure to a variety of models, they develop the strong mental images that they will need to succeed in math.
Beth Wycoff, using Woot Math with all her 5-7th grade students, found:
“Woot Math has given me a practical and efficient way to take students individually from concrete to abstract understanding of fraction concepts. Students are able to construct fractions and visualize the problems they are solving.”
Adaptive Learning Platform
The promise of adaptive technology is the ability for software to tailor content to each individual student’s needs. But not all adaptive platforms (also known as personalized learning environments) adapt in the same way. In fact, there are huge variations in the adaptivity and recommendations that these systems can make. The Woot Math platform analyzes student work – not just a right or wrong answer – but their actual interactions with the models, manipulatives, and scratchpad. Because the adaptive platform understands the student’s interaction with each problem, it can make much more targeted decisions about what the student knows, what the student doesn’t know, and what gaps to help remediate. From our
NSF-funded research, we know that our adaptive platform has shown dramatic improvements in student learning.
Get your students started today!
Want to Learn More?
Dr. Terry Wyberg of the Rational Number Project provides tangible advice and practical tips for helping your students develop number sense in his article,
Adding Fractions: Unlocking Confidence & Flexibility.